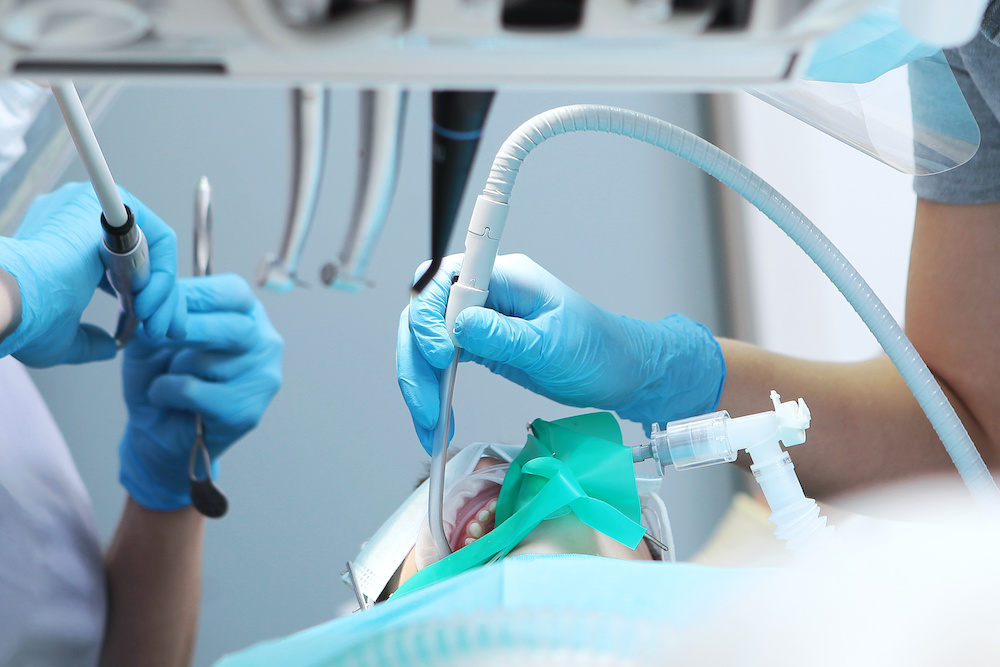
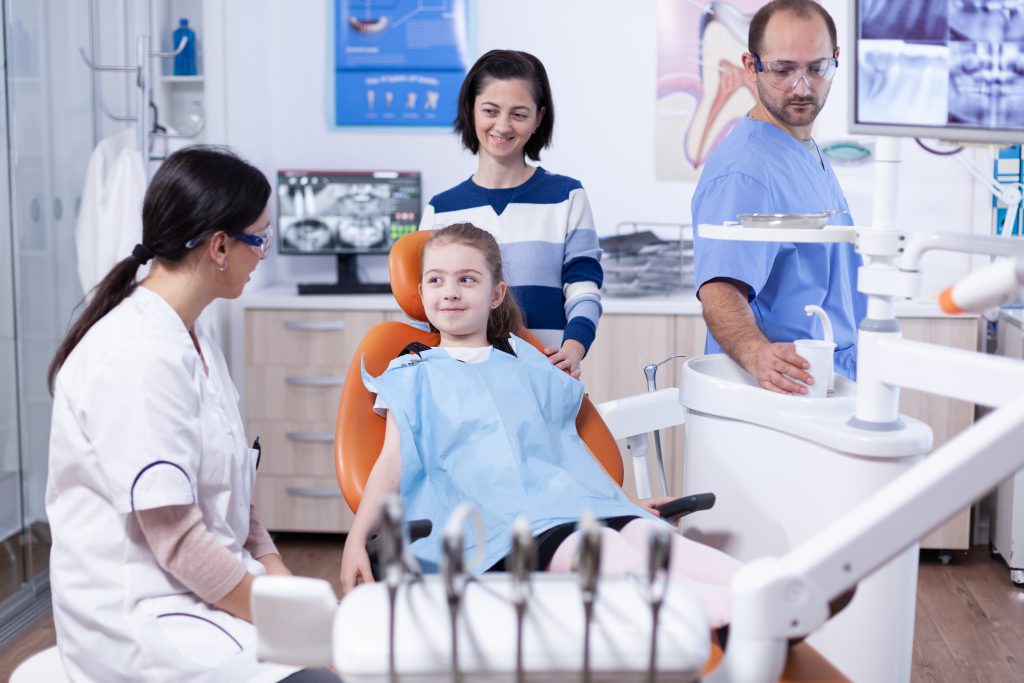
When it comes to pediatric dental procedures, the thought of putting your child under anesthesia can be concerning. However, it’s important to understand the difference between General Anesthesia and Oral Sedation, so you can make informed decisions about your child’s dental care.
General Anesthesia, also known as “sleep dentistry,” involves administering medication that puts your child into a deep sleep. During this time, they will be unable to feel or remember any sensations or sounds during the procedure. General Anesthesia is often used for longer, more complex procedures, such as multiple extractions or extensive restorative treatments.
On the other hand, Oral Sedation involves the use of a mild sedative, usually in the form of a pill, that helps your child feel relaxed and calm during their dental procedure. Unlike General Anesthesia, your child will be awake and able to respond to commands during the procedure, but they may feel groggy or have a limited memory of the event. Oral Sedation is often used for shorter procedures or for children who are anxious or have special needs.
Both General Anesthesia and Oral Sedation have their own benefits and risks, and the best option for your child will depend on the nature of their procedure, their individual needs and comfort level, and other factors. Your pediatric dentist will work with you to determine the best approach for your child and ensure their safety and comfort throughout the procedure.
In conclusion, it’s important to understand the difference between General Anesthesia and Oral Sedation in pediatric dentistry, so you can make informed decisions about your child’s dental care. By working closely with your pediatric dentist, you can ensure that your child receives the best care possible, in a safe and comfortable environment.